How does the Water Pump Motor Stator and Rotor Core interact with cooling systems, such as liquid or air-cooled housings, to maintain optimal temperature balance during intensive operation?
-
Thermal Transfer Efficiency and Heat Dissipation Dynamics:
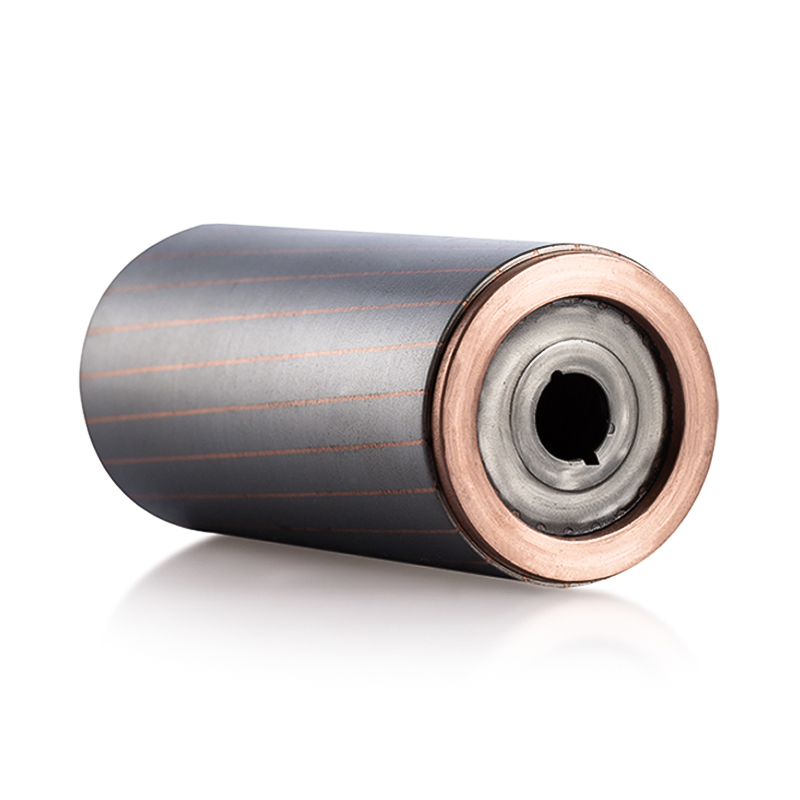
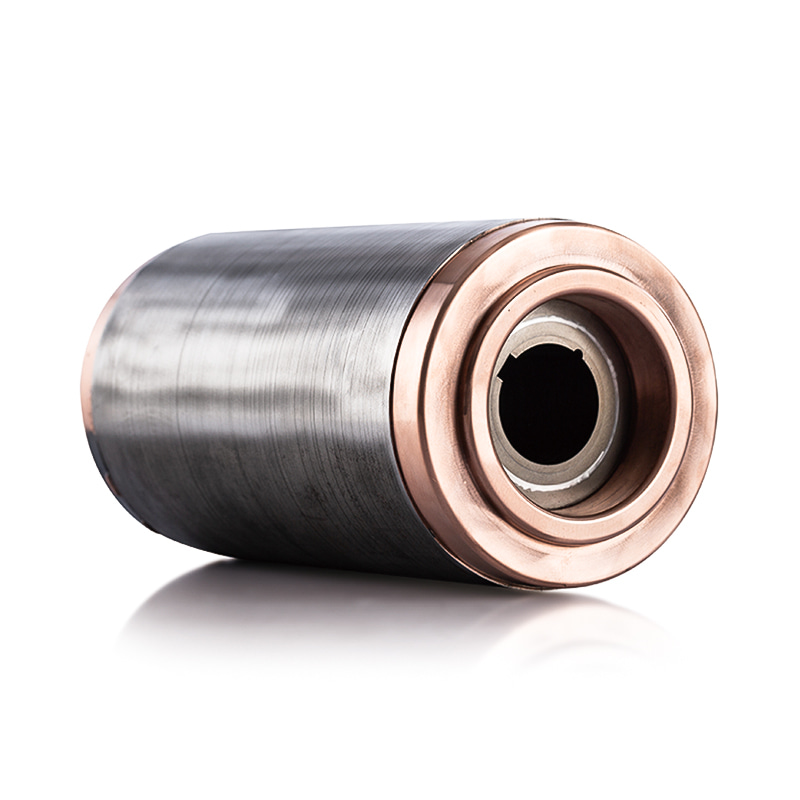
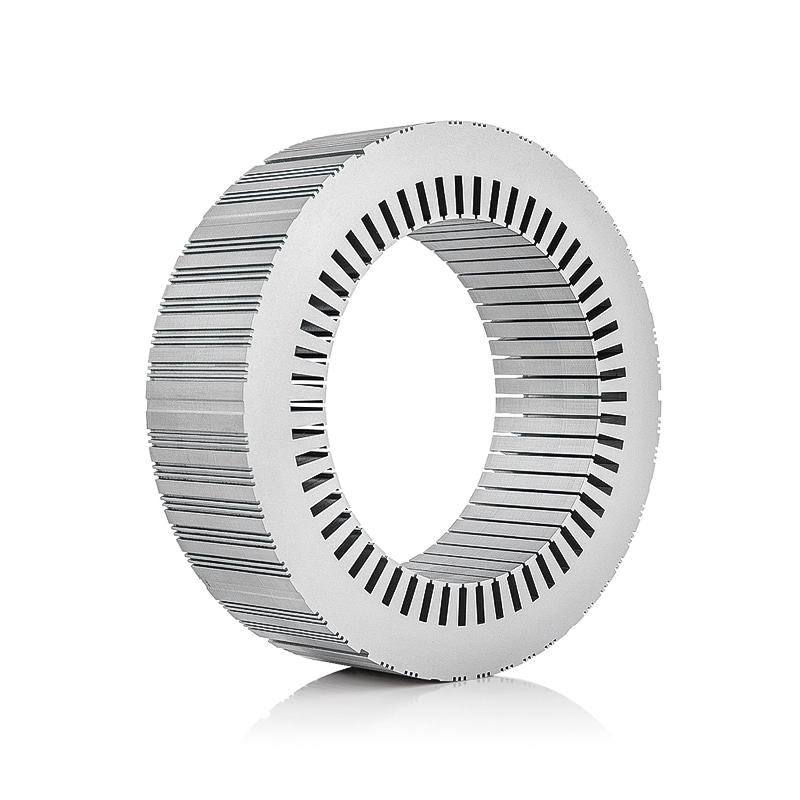
The Water Pump Motor Stator and Rotor Core are continuously exposed to heat generated during magnetic field excitation and current flow. Efficient heat dissipation is essential to prevent demagnetization or insulation degradation. The cores are composed of high-quality laminated silicon steel with superior thermal conductivity, ensuring rapid heat transfer away from the magnetic circuit. When paired with a liquid-cooled housing, coolant flows through integrated channels that directly contact high-temperature zones, promoting even thermal distribution. In air-cooled systems, the inclusion of optimized ventilation pathways and heat-dissipating fins helps maximize airflow around the stator and rotor assembly. The result is a controlled temperature gradient that prevents thermal hotspots and preserves the uniform magnetic performance of the motor. -
Design and Engineering of Cooling Pathways:
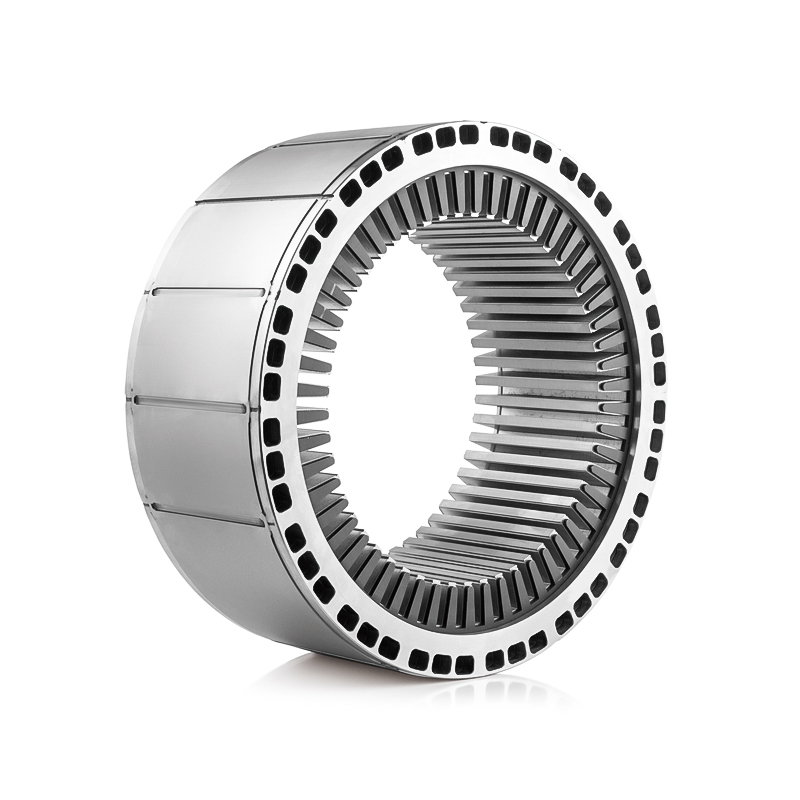
The layout of the cooling system determines how effectively the Water Pump Motor Stator and Rotor Core can maintain stable operating temperatures. In liquid-cooled designs, internal cooling jackets or spiral channels are positioned close to the stator windings and rotor shaft to ensure efficient convection and minimize heat accumulation. Advanced computational fluid dynamics (CFD) modeling is often employed to simulate flow velocity, turbulence, and temperature gradients within these channels. For air-cooled configurations, engineered fan systems or forced ventilation ducts are designed to direct air evenly across the stator slots and rotor periphery, reducing localized heating and maintaining consistent motor torque. The overall goal of both designs is to preserve the electromagnetic balance and reduce mechanical strain caused by temperature variations. -
Material Compatibility and Thermal Expansion Coordination:
The interaction between the Water Pump Motor Stator and Rotor Core and the cooling system materials must account for differences in thermal expansion. The motor components, including laminations, copper windings, and insulation layers, expand at varying rates under heat. Improper management of these differences can lead to mechanical stress, misalignment, or even cracking. Engineers use precise material selection and dimensional tolerances to ensure that all parts expand uniformly under operational temperatures. Thermal interface materials (TIMs) and specialized adhesives with high thermal conductivity but low expansion coefficients are used between the stator core and cooling surfaces to facilitate consistent contact and reduce vibration-related heat buildup. This balance prevents mechanical deformation and ensures the rotor’s concentric alignment with the stator bore remains intact throughout operation. -
Preservation of Electromagnetic and Magnetic Flux Stability:
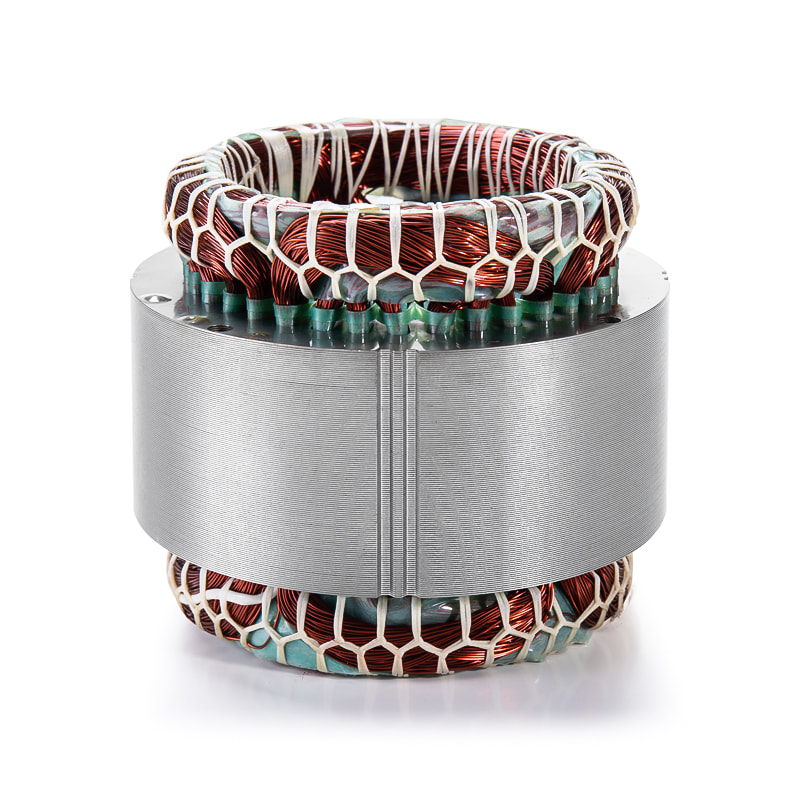
The magnetic efficiency of the Water Pump Motor Stator and Rotor Core is directly affected by temperature. As temperature increases, magnetic permeability may decrease, resulting in reduced flux density and lower torque output. An effective cooling system stabilizes these thermal conditions, allowing magnetic domains to maintain consistent alignment. This stability translates to uniform torque generation, reduced electrical losses, and minimal rotor imbalance. Modern insulation coatings on stator laminations help reduce eddy current losses by maintaining electrical isolation even under elevated temperatures, further supporting electromagnetic efficiency. -
Integration with Advanced Thermal Monitoring and Control Systems:
To enhance the reliability of the Water Pump Motor Stator and Rotor Core, contemporary motor systems integrate thermal sensors and control electronics within the stator windings and housing. These sensors constantly monitor temperature at multiple points, feeding data into a real-time control algorithm. When excessive heat is detected, the system automatically adjusts cooling intensity—by increasing coolant flow rate or fan speed—to restore thermal equilibrium. In high-performance applications, predictive thermal control algorithms can forecast potential overheating trends based on load conditions and adjust cooling proactively. This intelligent feedback loop ensures consistent performance without energy wastage or unnecessary mechanical wear.
 简体中文
简体中文 English
English русский
русский Español
Español