520-350 Elevator Motor
Stator inner and outer diameter: 520-350 Number of stator slots: 36 slots ...
The elevator traction motor is a crucial component in the operation of modern elevators, responsible for converting electrical energy into mechanical energy to move the elevator cab. It consists of two main parts: the stator and the rotor core.
The stator is the stationary part of the motor, typically composed of a series of laminated steel sheets stacked together. These laminations reduce energy losses due to eddy currents and improve efficiency. The stator houses the windings through which electrical current flows, generating a magnetic field. This magnetic field interacts with the rotor, producing the torque necessary to drive the elevator.
The rotor core, on the other hand, is the rotating part of the motor. It is also made from laminated steel, which helps to minimize losses and enhance performance. The rotor typically has conductive bars or coils that allow it to react to the magnetic field generated by the stator. As the magnetic field fluctuates, it induces currents in the rotor, causing it to turn and, in turn, drive the elevator mechanism.
Together, the stator and rotor core work in harmony to ensure smooth and efficient operation of the elevator, providing reliable transportation within buildings. The design and materials used in both components play a significant role in the motor's overall performance, durability, and energy efficiency.

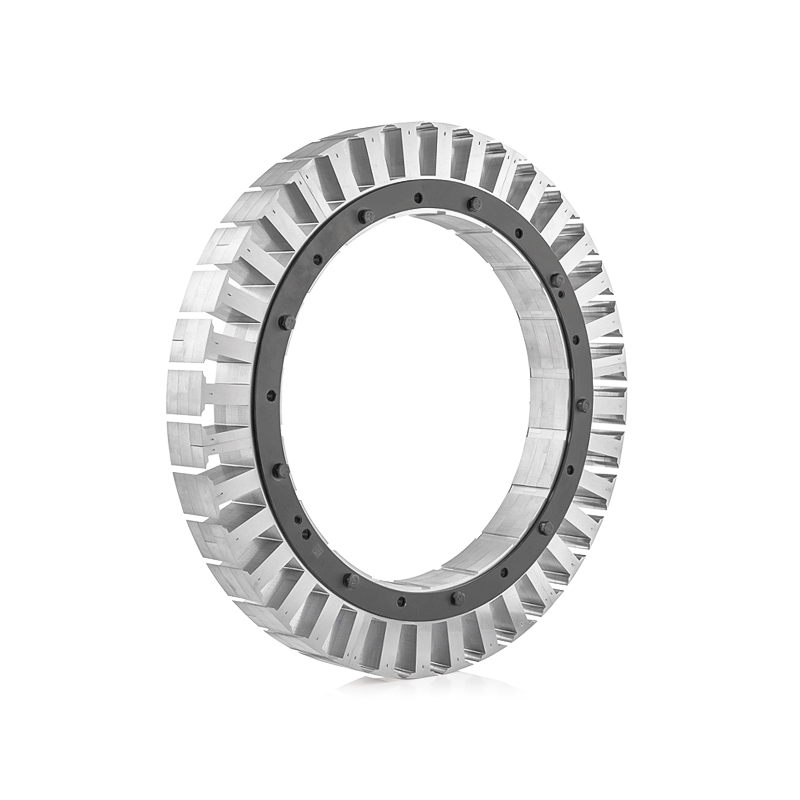
Stator inner and outer diameter: 520-350 Number of stator slots: 36 slots ...
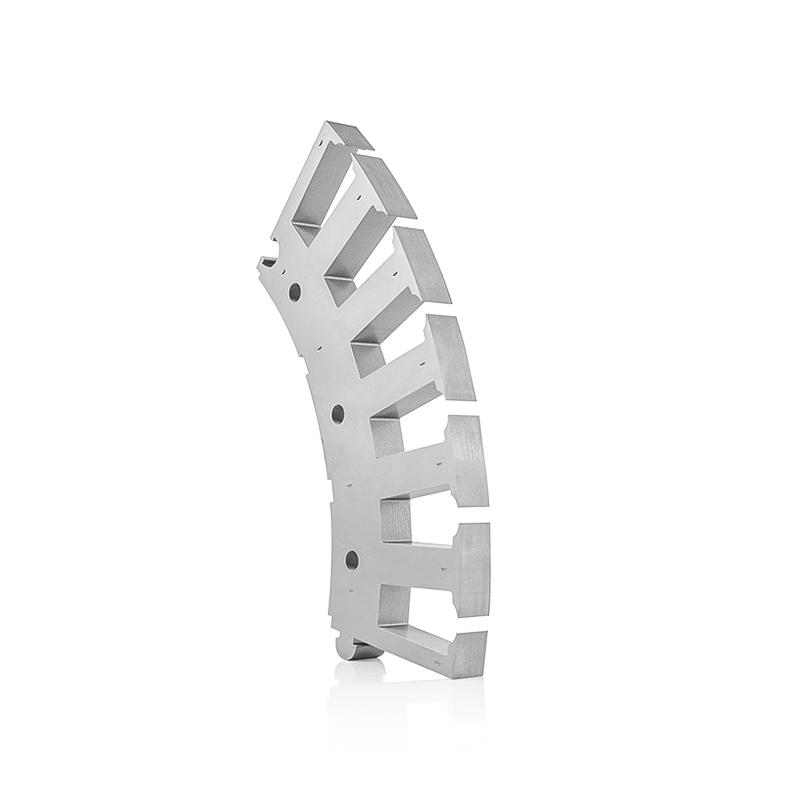

Stator inner and outer diameter: 520-350 Number of stator slots: 36 slots ...
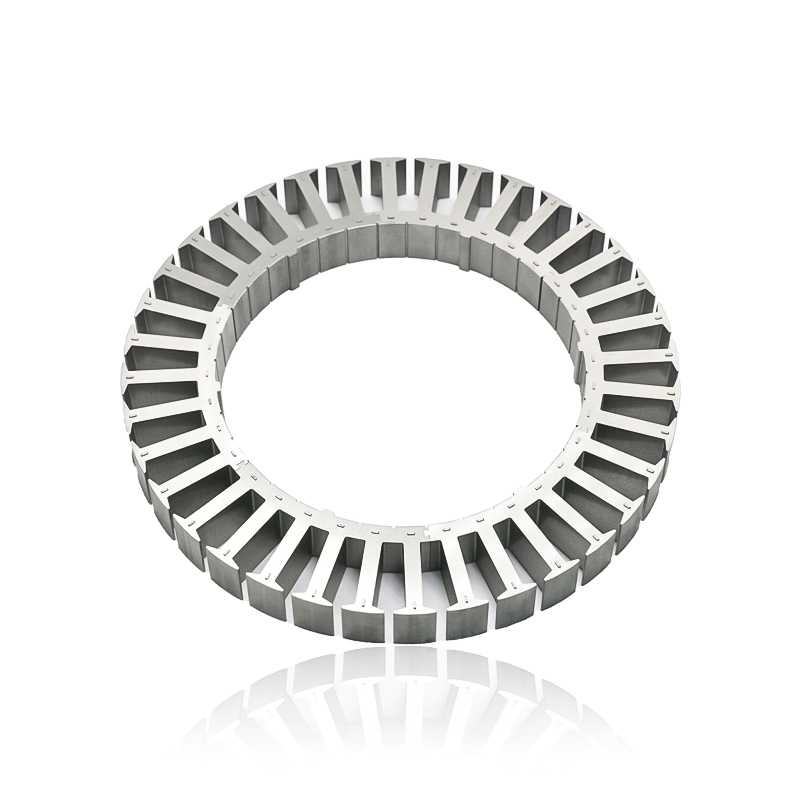

Performance under thermal cycling: Automotive motors are subjected to frequent heating and cooling cycles due to variations in load, ambient temperature, and motor operation. Automotive Motor Stator Cores, typically made of laminated electrical steel, must maintain structural integrity and magneti...
View MoreFundamental Role of Magnetic Flux Density: Magnetic flux density (B) in Wind Power Generator Motor Stator Core is a fundamental parameter that determines the strength of the magnetic field within the stator core and the effectiveness of energy conversion from mechanical to electrical form. Higher ...
View MoreCore Loss Mechanisms in the Stator Core: The stator core of a wind power generator experiences energy losses primarily through hysteresis and eddy current effects, which are inherent to the operation of ferromagnetic materials under alternating magnetic fields. Hysteresis loss occurs as the magnet...
View More