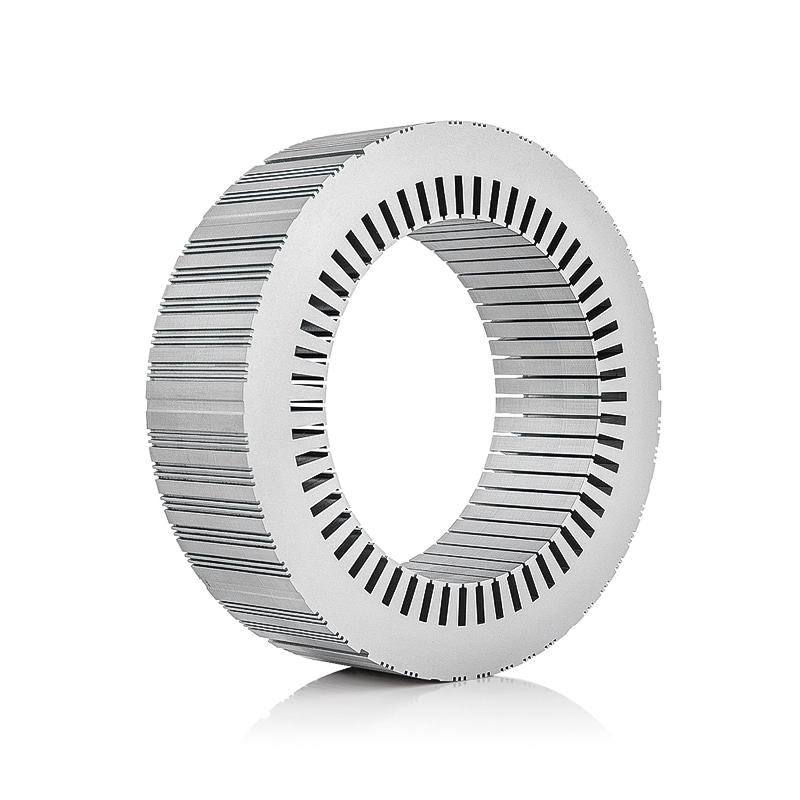
How does the design of the Electric Vehicle Generator Motor Stator and Rotor Core contribute to the overall efficiency of the motor in generating power for the vehicle?
Magnetic Flux Optimization
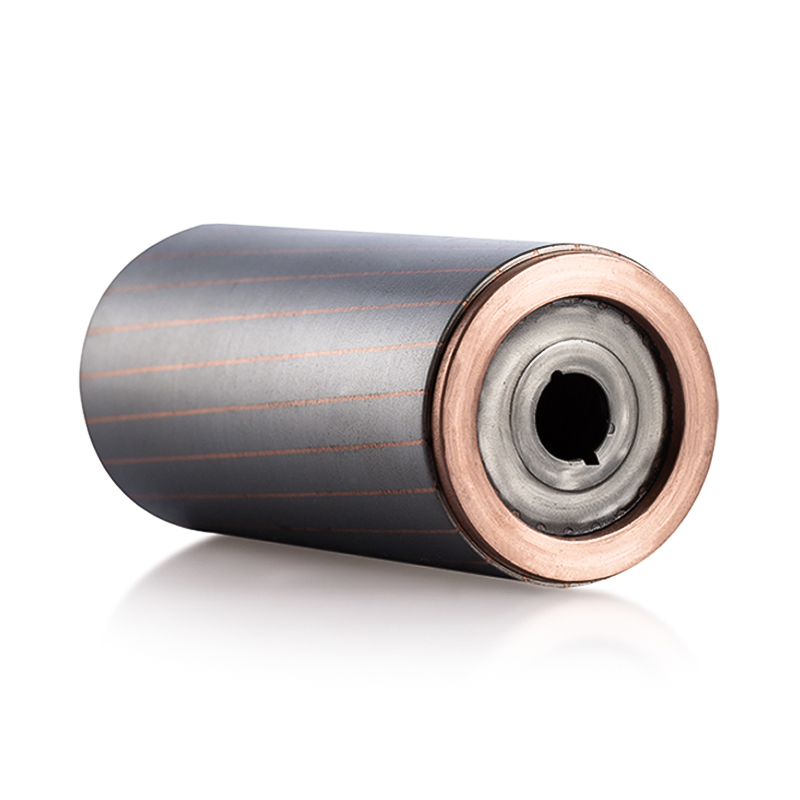
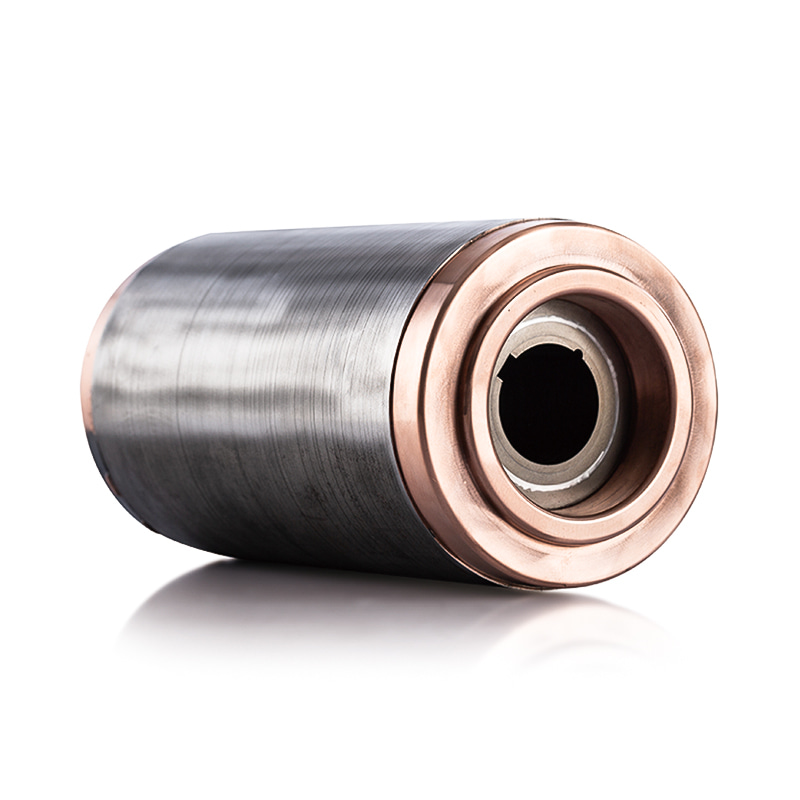
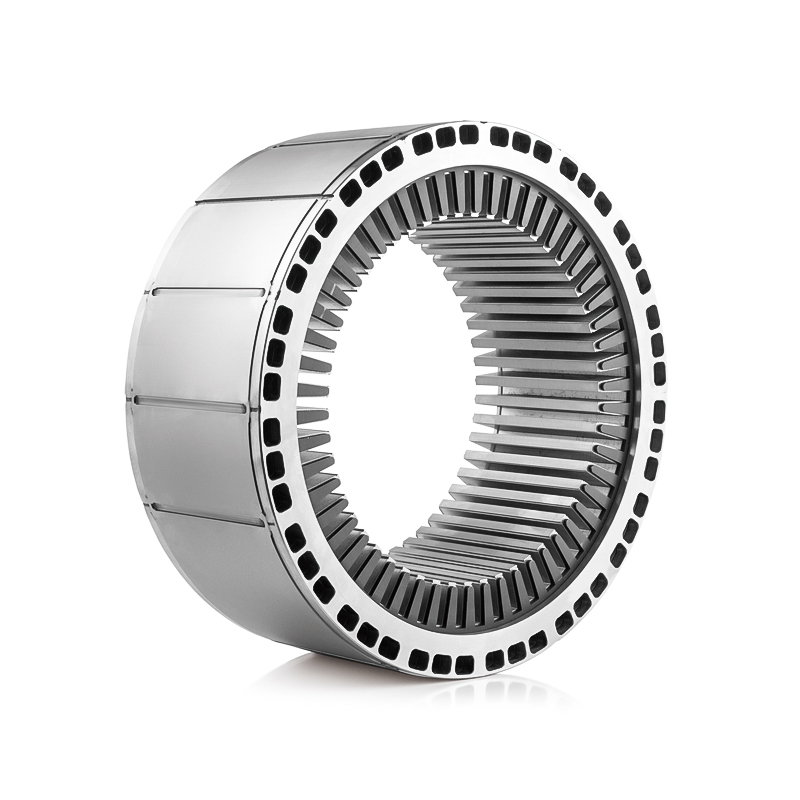
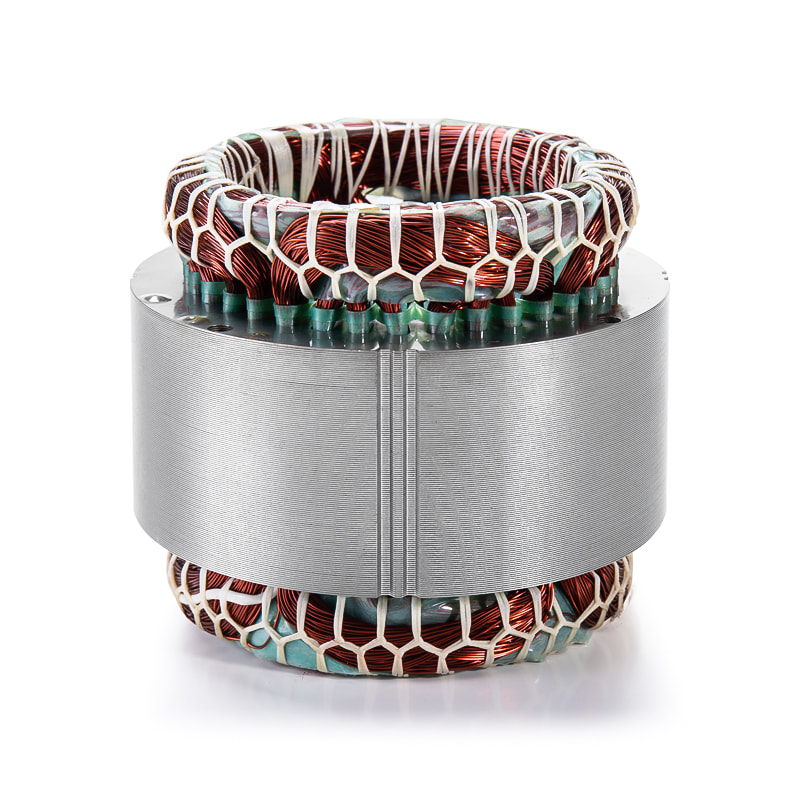
The Electric Vehicle Generator Motor Stator and Rotor Core are designed to efficiently generate and channel magnetic flux within the motor. The stator, typically made from laminated sheets of silicon steel, forms the stationary part of the motor, while the rotor, often consisting of a set of permanent magnets or wound coils, rotates inside the stator. The primary function of these components is to generate a rotating magnetic field that induces electric currents, which ultimately drive the motor.
A well-designed stator and rotor core will have optimal magnetic flux paths, meaning the flux lines are directed with minimal resistance or leakage. This reduces energy losses due to inefficiencies in the magnetic field and maximizes the overall output. A highly optimized magnetic field within the motor leads to better conversion of electrical energy into mechanical energy, improving the overall efficiency of the vehicle’s powertrain.
Minimizing Eddy Current Losses
Eddy current losses occur when a changing magnetic field induces currents within the conductive material of the stator and rotor, which then dissipate as heat. The design of the Electric Vehicle Generator Motor Stator and Rotor Core is critical in minimizing these losses. To achieve this, manufacturers use laminated cores for the stator and rotor. The laminations are thin, insulating layers of metal that reduce the size and effect of eddy currents, thereby decreasing energy losses and improving the overall efficiency of the motor.
The thickness and material composition of these laminations are optimized for low resistivity and minimal core losses. By reducing eddy currents, the motor generates more power with less energy waste, significantly enhancing efficiency.
Core Material Selection
The materials used for the stator and rotor core are crucial for improving the motor's efficiency. Silicon steel, commonly used for the stator, offers excellent magnetic properties with low core loss, which directly translates into higher efficiency in the power generation process. Higher-grade materials, such as cobalt or iron alloys, may also be used in high-performance applications to further improve the magnetic permeability and reduce losses.
Additionally, the use of permanent magnets in the rotor (if applicable) can significantly boost motor efficiency. High-quality magnets, like neodymium magnets, provide a strong and consistent magnetic field, reducing the need for additional energy input to generate power, making the rotor more efficient.
Optimal Stator and Rotor Geometry
The shape, size, and geometry of the stator and rotor cores are carefully designed to minimize losses and maximize the motor's torque and power density. The number of poles, winding configuration, and slot design of the stator are all tailored to ensure that the motor operates with minimal losses at a wide range of speeds and loads. These design parameters determine the efficiency of the electromagnetic coupling between the stator and rotor, which directly affects how effectively the motor can generate power.
In the rotor, slot winding configurations are designed to reduce resistance, minimize harmonics, and optimize torque output. A rotor with optimized geometry and high-quality windings will ensure that the motor produces consistent power while maintaining low energy losses.
Cooling and Heat Management
As the Electric Vehicle Generator Motor Stator and Rotor Core generate power, they also produce heat, which can affect the motor's efficiency and performance over time. A well-designed cooling system is essential for maintaining optimal temperature levels within the motor. Many modern motors incorporate liquid or air cooling systems around the stator and rotor cores to dissipate excess heat, ensuring that the motor operates within an efficient temperature range.
Efficient heat dissipation prevents overheating, which could otherwise cause the motor to lose efficiency or even fail prematurely. In turn, this cooling mechanism extends the lifespan of the stator and rotor cores while maintaining their performance over long periods of operation.
Rotor-Stator Interaction and Air Gap Optimization
The air gap between the stator and rotor is another critical factor in the design of an efficient Electric Vehicle Generator Motor Stator and Rotor Core. The smaller and more uniform the air gap, the more effectively the magnetic flux can be transmitted between the rotor and stator. By minimizing the air gap, the motor can generate higher torque at lower speeds, making it more efficient across a wider range of driving conditions.
Precise manufacturing of the rotor and stator cores ensures that the air gap is uniform and optimized, which reduces the possibility of magnetic field loss and improves power generation efficiency. Even small variations in the air gap can result in significant performance losses, so careful attention to this detail is essential.
Reduced Noise and Vibration
Efficient Electric Vehicle Generator Motor Stator and Rotor Core designs also focus on reducing mechanical vibrations and acoustic noise. Vibrations within the motor can lead to energy losses and affect the overall motor performance. By ensuring that the rotor is balanced and that the stator laminations are correctly aligned, designers can minimize vibrations that would otherwise waste energy and reduce efficiency. Noise reduction also contributes to the overall comfort of the vehicle by lowering operational noise, which is an important consideration in electric vehicle design.
Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) Minimization
The Electric Vehicle Generator Motor Stator and Rotor Core design must account for electromagnetic interference (EMI), which can disrupt the vehicle's electrical systems and reduce efficiency. Proper shielding, insulation, and grounding in the motor's design help reduce EMI, ensuring that the motor’s power generation does not interfere with other critical vehicle components, such as sensors, communications, and onboard electronics. A well-designed core ensures stable performance without interference, contributing to the overall operational efficiency of the vehicle.
Energy Recovery and Regenerative Braking
One of the most important functions of the Electric Vehicle Generator Motor Stator and Rotor Core is its ability to participate in regenerative braking. During regenerative braking, the motor acts as a generator, converting kinetic energy back into electrical energy, which is then stored in the vehicle’s battery. The design of the stator and rotor cores must support efficient power conversion during braking events to maximize the energy recovery process. By utilizing high-efficiency materials, optimizing core geometry, and ensuring the rotor and stator work in tandem with the power electronics, regenerative braking can be more effective, increasing the overall energy efficiency of the vehicle.
 简体中文
简体中文 English
English русский
русский Español
Español