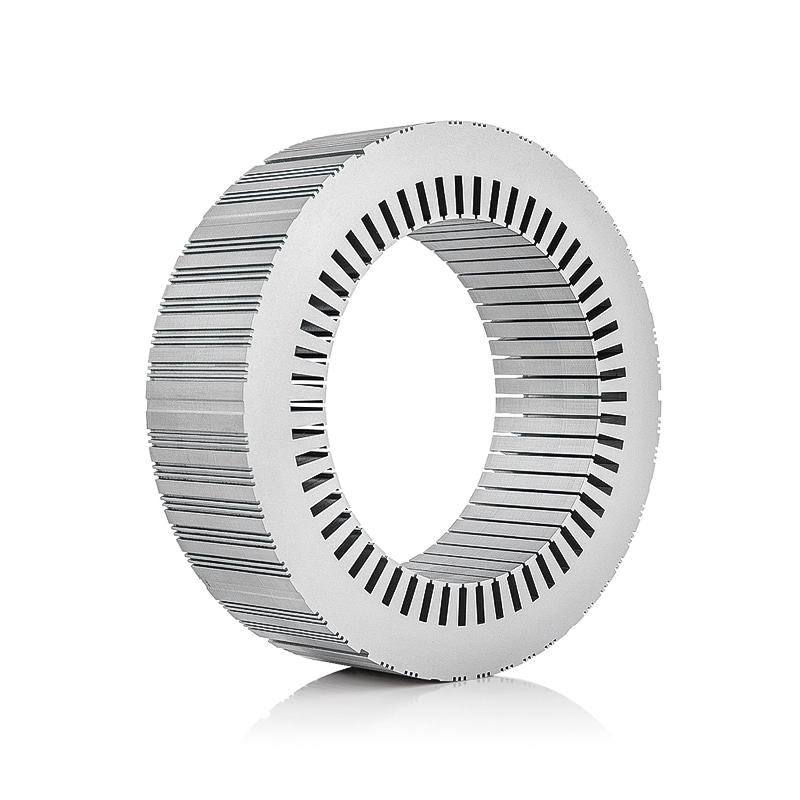
How does the lamination thickness and stacking technique in the Electric Vehicle Drive Motor Rotor Core affect efficiency and thermal management?
Understanding Lamination Thickness in Electric Vehicle Drive Motor Rotor Cores
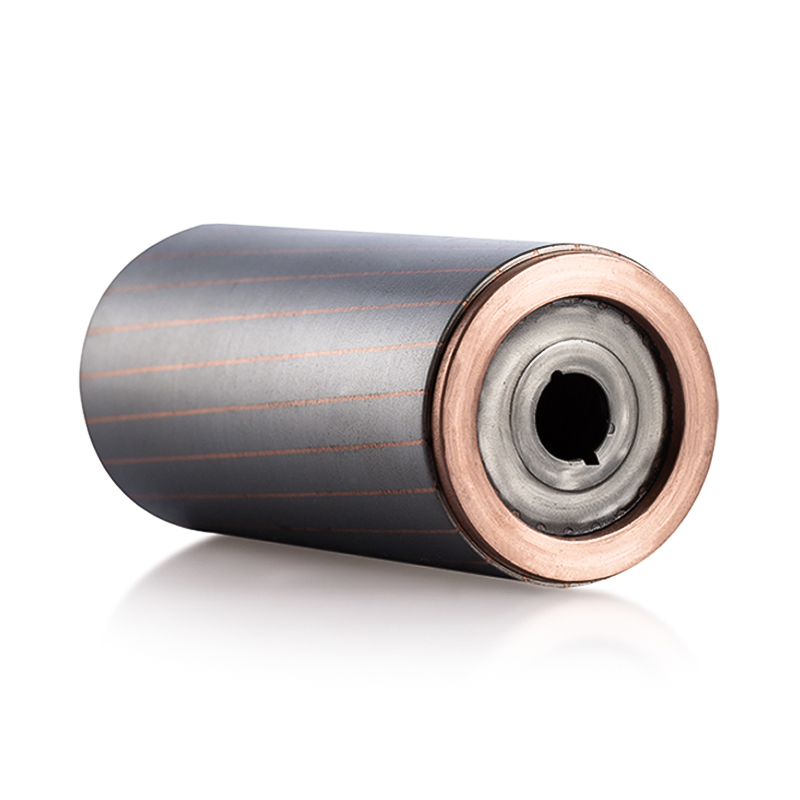
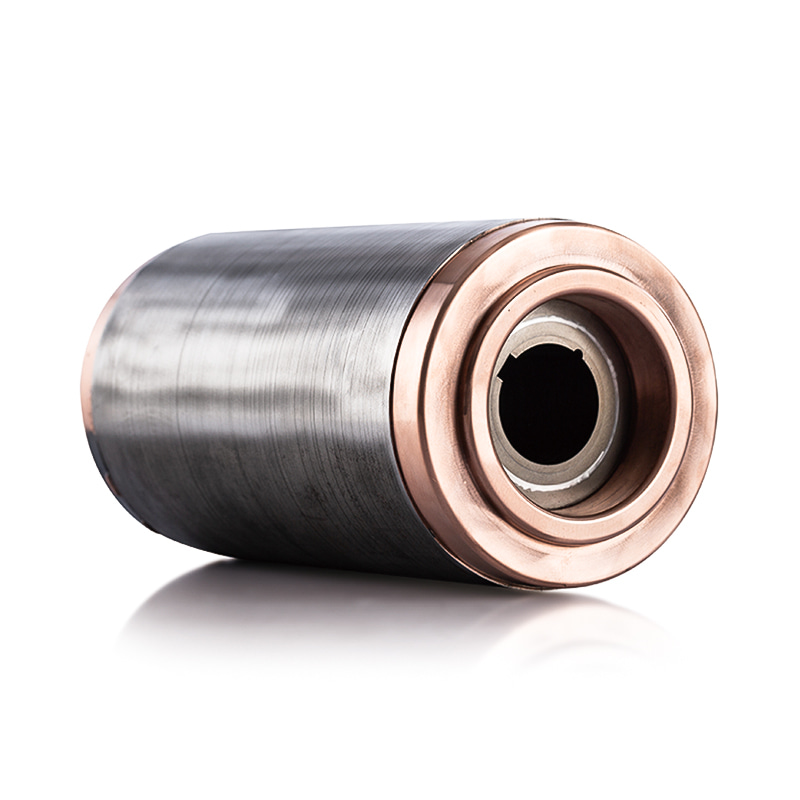
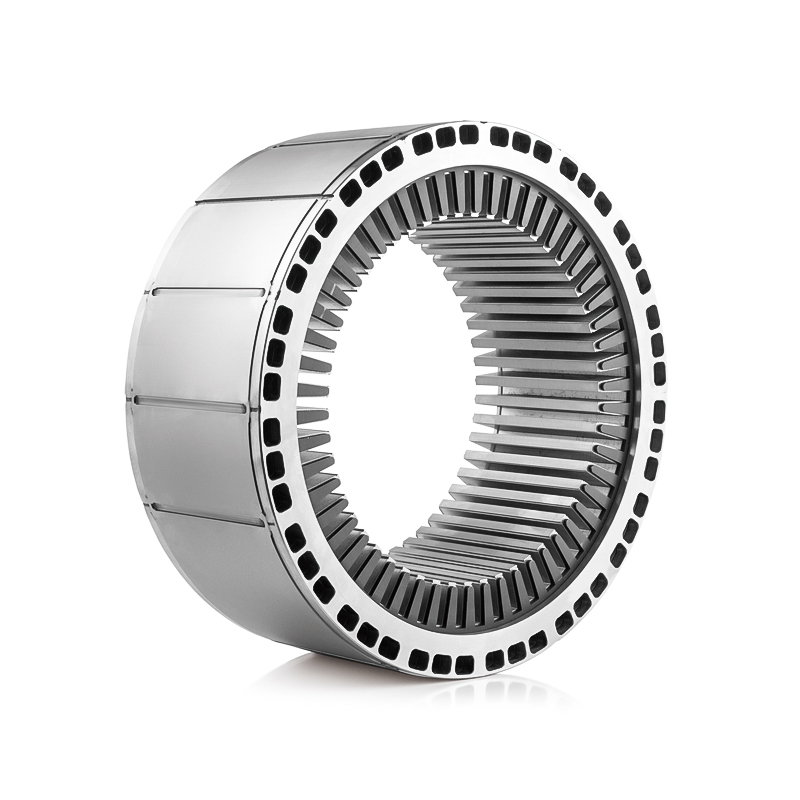
The rotor core in electric vehicle drive motor is typically constructed from a series of thin, laminated steel sheets that are stacked together to form a magnetically conductive structure. The thickness of these laminations is a critical parameter because it directly influences eddy current losses, which are currents induced in the conductive material by alternating magnetic fields. Thicker laminations increase the path length for these currents, resulting in higher circulating currents and significant heat generation within the rotor. Excessive heat can degrade the magnetic properties of the steel, reduce overall motor efficiency, and accelerate insulation wear in adjacent components. On the other hand, extremely thin laminations reduce eddy current losses, improving efficiency and reducing thermal buildup. However, thinner laminations also require greater precision during manufacturing and assembly, as misalignment or inconsistent thickness can create localized magnetic flux leakage or mechanical weakness. Therefore, engineers must carefully balance lamination thickness to minimize electrical losses while maintaining manufacturability, structural integrity, and cost-effectiveness, ensuring that the rotor operates efficiently under varying loads and speeds without excessive heat generation.
Stacking Techniques and Their Impact on Rotor Performance
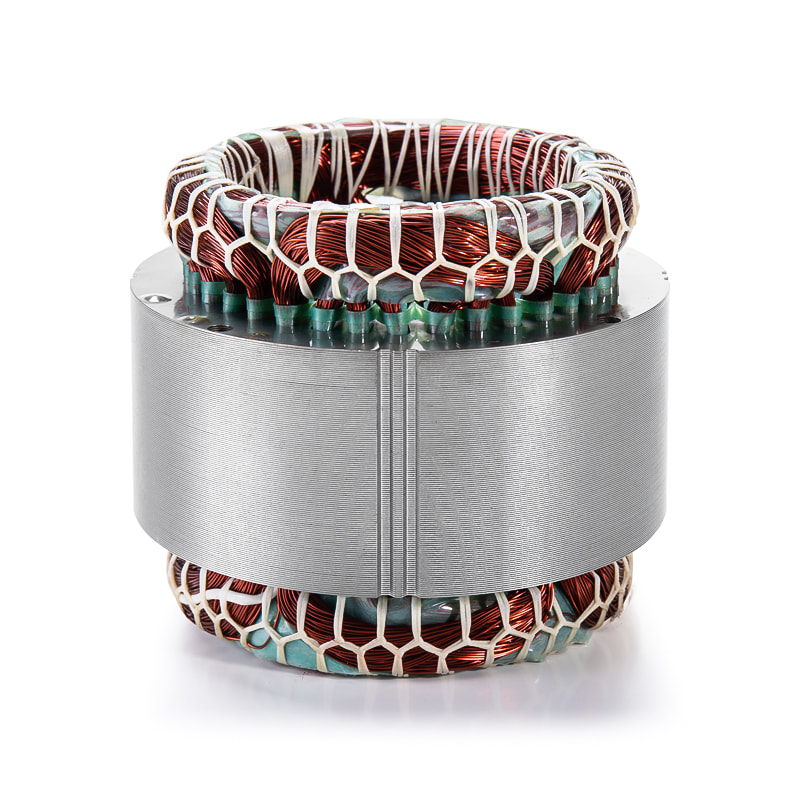
The stacking technique of the laminations is equally important for the performance and durability of the rotor core. Laminations are typically joined through methods such as butted joints, welding, adhesive bonding, or interlocking shapes, which maintain alignment and mechanical stability under high-speed rotation. Proper stacking minimizes air gaps and misalignment that can cause flux leakage, localized eddy currents, and uneven heating within the rotor. Advanced stacking techniques, such as skewed or segmented stacking, are sometimes employed to reduce cogging torque, improve torque smoothness, and enhance thermal distribution. Skewed laminations, for example, reduce harmonic flux variations in the rotor, which minimizes vibration, noise, and localized heating. In addition, precise stacking ensures that the rotor can withstand centrifugal forces generated at high rotational speeds without deformation. By ensuring uniform alignment and contact between laminations, these stacking techniques allow heat to conduct efficiently through the rotor core, contributing to more effective thermal management and stable magnetic performance during prolonged operation.
Thermal Management and Efficiency Considerations
Thermal management is a critical concern for electric vehicle drive motors, where the rotor operates continuously under varying load conditions, from low-speed torque demand to high-speed efficiency operation. Heat generated in the rotor core arises from both eddy current and hysteresis losses, and improper lamination thickness or misaligned stacking can create hotspots that impair magnetic performance and accelerate material degradation. Optimal lamination thickness, combined with precise stacking, ensures that heat is distributed evenly throughout the rotor and conducted efficiently to the stator or cooling system. This reduces temperature gradients that could otherwise lead to thermal stress, mechanical deformation, or loss of efficiency. In addition, efficient thermal management helps maintain the magnetic saturation point of the rotor material, ensuring that torque density, energy conversion efficiency, and overall motor performance remain consistent over time. By carefully designing lamination and stacking parameters, manufacturers can achieve a balance between minimizing electrical losses, maintaining structural integrity, and ensuring effective heat dissipation, all of which are essential for the reliable, high-performance operation of electric vehicle drive motors.
Mechanical Integrity and Longevity
The combination of lamination thickness and stacking technique also affects the mechanical integrity and lifespan of the rotor core. During high-speed operation, the rotor experiences centrifugal forces that place significant stress on the laminated structure. Improper stacking or overly thin laminations can lead to deformation, delamination, or mechanical fatigue, which compromise efficiency and could cause catastrophic failure over time. By optimizing both the lamination thickness and the stacking method, engineers ensure that the rotor maintains its shape, alignment, and structural stability throughout its operational life. This not only preserves efficiency but also prevents vibrations, noise, and premature wear in the overall motor assembly. Furthermore, precise lamination and stacking facilitate maintenance of consistent magnetic properties, ensuring predictable torque output, smooth acceleration, and reliable performance under all operating conditions, which are critical for electric vehicle drivability, energy efficiency, and component longevity.
 简体中文
简体中文 English
English русский
русский Español
Español